Python is a powerfull scripting language which is using for many automation purpose in system management . In this blog i am introducing a python module called boto (boto3) for AWS management purpose like creating instances, S3 bucket's , transferring files to S3 bucket etc..
Boto is the Amazon Web Services (AWS) SDK for Python, which allows Python developers to write software that makes use of Amazon services like S3 and EC2. Boto provides an easy to use, object-oriented API as well as low-level direct service access.
1. Installing the boto3 in your local system
First install the python-pip which is used to install boto3
*************************************************
unixchips@unixchips:~$ sudo apt install python-pip
[sudo] password for unixchips:
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required:
linux-headers-4.10.0-28 linux-headers-4.10.0-28-generic
linux-headers-4.13.0-32 linux-headers-4.13.0-32-generic
linux-headers-4.13.0-36 linux-headers-4.13.0-36-generic
linux-headers-4.13.0-37 linux-headers-4.13.0-37-generic
linux-headers-4.13.0-38 linux-headers-4.13.0-38-generic
linux-headers-4.13.0-39 linux-headers-4.13.0-39-generic
linux-headers-4.13.0-41 linux-headers-4.13.0-41-generic
linux-headers-4.13.0-43 linux-headers-4.13.0-43-generic
linux-headers-4.15.0-29 linux-headers-4.15.0-29-generic
linux-headers-4.15.0-30 linux-headers-4.15.0-30-generic
linux-image-4.10.0-28-generic linux-image-4.13.0-32-generic
linux-image-4.13.0-36-generic linux-image-4.13.0-37-generic
linux-image-4.13.0-38-generic linux-image-4.13.0-39-generic
linux-image-4.13.0-41-generic linux-image-4.13.0-43-generic
linux-image-4.15.0-24-generic linux-image-4.15.0-29-generic
linux-image-4.15.0-30-generic linux-image-extra-4.10.0-28-generic
linux-image-extra-4.13.0-32-generic linux-image-extra-4.13.0-36-generic
linux-image-extra-4.13.0-37-generic linux-image-extra-4.13.0-38-generic
linux-image-extra-4.13.0-39-generic linux-image-extra-4.13.0-41-generic
linux-image-extra-4.13.0-43-generic linux-image-extra-4.13.0-45-generic
linux-modules-4.15.0-24-generic linux-modules-4.15.0-29-generic
linux-modules-4.15.0-30-generic
...........................................................
Now we have to install awscli ( command line tool for aws management) and boto3 using below command unixchips@unixchips:~$ pip install awscli boto3 -U --ignore-installed six
Collecting awscli
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/e6/8e/129966e5ae7e14a301fe58e81b7ce6dd762745518b6e3f987fb1d1df55a1/awscli-1.16.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (1.3MB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 1.3MB 654kB/s
Collecting boto3
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d6/bc/5393e095b03e871055efae27bac7d314c7f62ab05fea098441052c2afdbb/boto3-1.8.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (128kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 133kB 1.8MB/s
Collecting six
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/67/4b/141a581104b1f6397bfa78ac9d43d8ad29a7ca43ea90a2d863fe3056e86a/six-1.11.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Collecting docutils>=0.10 (from awscli)
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/50/09/c53398e0005b11f7ffb27b7aa720c617aba53be4fb4f4f3f06b9b5c60f28/docutils-0.14-py2-none-any.whl (543kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 552kB 1.2MB/s
Collecting PyYAML<=3.13,>=3.10 (from awscli)
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/9e/a3/1d13970c3f36777c583f136c136f804d70f500168edc1edea6daa7200769/PyYAML-3.13.tar.gz (270kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 276kB 1.9MB/s
Collecting s3transfer<0.2.0,>=0.1.12 (from awscli)
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d7/14/2a0004d487464d120c9fb85313a75cd3d71a7506955be458eebfe19a6b1d/s3transfer-0.1.13-py2.py3-none-any.whl (59kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 61kB 4.0MB/s
Collecting rsa<=3.5.0,>=3.1.2 (from awscli)
Downloading https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/e1/ae/baedc9cb175552e95f3395c43055a6a5e125ae4d48a1d7a924baca83e92e/rsa-3.4.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl (46kB)
100% |████████████████████████████████| 51kB 3.4MB/s
Collecting colorama<=0.3.9,>=0.2.5 (from awscli)
*************************************************************
2. Next step is to create a user with programmatic access in AWS . This user should give full permission with respect to EC2, S3, RDS level . Go to services-IAM-users and click add user option
3. Now copy the access-key and secret-access-key of the newly created user from IAM-user-security credentials and paste it in ~.aws/credentials
unixchips@unixchips:~/.aws$ cat credentials
[default]
aws_access_key_id = ************
aws_secret_access_key = **************************
(set the permission for the credential file so that other's doesn't have access on it)
Script to find EC2 status
For sample testing i have created an EC2 instance and forcefully shutdown that, we will see how can we get the instance status using boto scriptsample Script
************************************************
unixchips@unixchips:~$ cat list_instances.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_ec2_client = session.client('ec2')
ec2 = boto3.resource('ec2')
for instance in ec2.instances.all():
print instance.id, instance.state
*************************************************
output:unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./list_instances.py
i-0fb8b62e337e1ab3f {u'Code': 80, u'Name': 'stopped'}
Create an instance using boto3
For creating the instance we need to give the AMI details which is using . So we have to pass the AMI details in the script
AMI id will be get as below from AWS console
sample script
***************************************************
unixchips@unixchips:~$ cat create_instances.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_ec2_client = session.client('ec2')
ec2 = boto3.resource('ec2')
instance = ec2.create_instances(
ImageId='ami-6cd6f714',
MinCount=1,
MaxCount=1,
InstanceType='t2.micro')
print instance[0].id
**************************************************
Output:
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./create_instances.py
i-039933493d9fbfa61
Also if we check the console we can see that one instance is created automatically
Script to terminate an instance
Now let us terminate an instance using the script
Sample script
******************************************************
unixchips@unixchips:~$ cat term_instance.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_ec2_client = session.client('ec2')
ec2 = boto3.resource('ec2')
for instance_id in sys.argv[1:]:
instance = ec2.Instance(instance_id)
response = instance.terminate()
print response
*******************************************************
In this case we need to pass the instance id as argument which we will get from list_instance.py script
output:
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./list_instances.py
i-039933493d9fbfa61 {u'Code': 16, u'Name': 'running'}
i-0fb8b62e337e1ab3f {u'Code': 80, u'Name': 'stopped'}
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./term_instance.py i-039933493d9fbfa61
{u'TerminatingInstances': [{u'InstanceId': 'i-039933493d9fbfa61', u'CurrentState': {u'Code': 32, u'Name': 'shutting-down'}, u'PreviousState': {u'Code': 16, u'Name': 'running'}}], 'ResponseMetadata': {'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'RequestId': '5fc8cc94-bc21-42a2-a673-82afaede516a', 'HTTPHeaders': {'transfer-encoding': 'chunked', 'content-type': 'text/xml;charset=UTF-8', 'vary': 'Accept-Encoding', 'date': 'Tue, 28 Aug 2018 20:20:34 GMT', 'server': 'AmazonEC2'}}}
Script to create the bucket
Now let's create a bucket using the boto script
Sample script
****************************************************
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_s3_client = session.client('s3')
s3 = boto3.resource('s3')
for bucket_name in sys.argv[1:]:
try:
response = s3.create_bucket(Bucket=bucket_name, CreateBucketConfiguration={
'LocationConstraint': 'us-west-2'})
print response
except Exception as error:
print error
*************************************************************
output:
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./create_s3.py pythonbucket1-$(date +%F-%s)
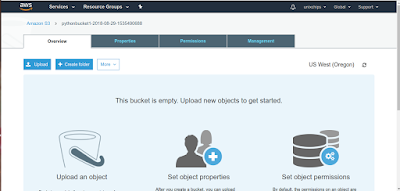
s3.Bucket(name='pythonbucket1-2018-08-29-1535490688')
From the console we can see that pythonbucket1 is created
Script to list all buckets and its contents
Sample script
********************************************************
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_s3_client = session.client('s3')
s3 = boto3.resource('s3')
for bucket in s3.buckets.all():
print bucket.name
print "---"
for item in bucket.objects.all():
print "\t%s" % item.key
***************************************************
Output:
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./list_s3.py
cf-templates-1heczgkj9avl7-ap-south-1
---
20181655Fc-autoscalv1.1gywvpp3fiw
20181657ke-designer/template1sgfsgkbkga8
2018165IdC-autoscalv1.2
20181661uh-ec2cloudformation.txt
201816657J-ec2cloudformation.txt
2018166Fiz-ec2cloudformation.txt
2018166UrA-ec2cloudformation
2018166V5J-ec2cloudformation
2018166VaD-ec2cloudformation.txt
2018166jfs-ec2cloudformation.txt
2018166kWD-ec2cloudformation.txt
2018166vPH-ec2cloudformation.txt
pythonbucket1-2018-08-29-1535490688
---
unixchips1
---
cloudformer.template
test1.txt
test3.txt
test4.txt
unixchips2
---
test2.txt
test3.txt
test4.txt
*****************************************************
Script to put a file to S3 bucket
sample script
************************************************************
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_s3_client = session.client('s3')
s3 = boto3.resource('s3')
bucket_name = sys.argv[1]
object_name = sys.argv[2]
try:
response = s3.Object(bucket_name, object_name).put(Body=open(object_name, 'rb'))
print response
except Exception as error:
print error
***********************************************
now let's create some text files
unixchips@unixchips:~$ touch file{1,2,3,4}.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 unixchips unixchips 0 Aug 29 12:30 file4.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 unixchips unixchips 0 Aug 29 12:30 file3.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 unixchips unixchips 0 Aug 29 12:30 file2.txt
-rw-rw-r-- 1 unixchips unixchips 0 Aug 29 12:30 file1.txt
output:
(we need to pass S3 bucket name and file details as parameters)
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./filecopy_s3.py pythonbucket1-2018-08-29-1535490688 file1.txt
{u'ETag': '"d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e"', 'ResponseMetadata': {'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HostId': 'H2f4CkfA/FOEhgrdsZtlKx62qtBZ5GpSBDkFnPmLiDxFKd/OWjsNhiu8jB8WuL/dRlwQUDvyZtI=', 'RequestId': '0495618196C7D050', 'HTTPHeaders': {'content-length': '0', 'x-amz-id-2': 'H2f4CkfA/FOEhgrdsZtlKx62qtBZ5GpSBDkFnPmLiDxFKd/OWjsNhiu8jB8WuL/dRlwQUDvyZtI=', 'server': 'AmazonS3', 'x-amz-request-id': '0495618196C7D050', 'etag': '"d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e"', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 07:01:06 GMT'}}}
Delete bucket contents
Sample script
*******************************************************
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_s3_client = session.client('s3')
s3 = boto3.resource('s3')
for bucket_name in sys.argv[1:]:
bucket = s3.Bucket(bucket_name)
for key in bucket.objects.all():
try:
response = key.delete()
print response
except Exception as error:
print error
******************************************************
output:-
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./delete_content_s3.py pythonbucket1-2018-08-29-1535490688
(we need to pass bucket name along with the script)
{'ResponseMetadata': {'HTTPStatusCode': 204, 'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HostId': '1oJ8Bs08KlxrEjbqEXVjgy7/U5EvySvxXf3wooMIZmOKGA9XzWc20K128fwrpsBkrB/qwIlsWvs=', 'RequestId': '2E0B2A932539FDE4', 'HTTPHeaders': {'x-amz-id-2': '1oJ8Bs08KlxrEjbqEXVjgy7/U5EvySvxXf3wooMIZmOKGA9XzWc20K128fwrpsBkrB/qwIlsWvs=', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 07:22:09 GMT', 'x-amz-request-id': '2E0B2A932539FDE4', 'server': 'AmazonS3'}}}
{'ResponseMetadata': {'HTTPStatusCode': 204, 'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HostId': '9Oc5R8xzAmrCJtd+EBeEQLosTRsJOH9LnEmZW5PzK3cDAkn3BCU1byvVmivpC3ssqS2Car/z/QM=', 'RequestId': '6B30F1635C22C516', 'HTTPHeaders': {'x-amz-id-2': '9Oc5R8xzAmrCJtd+EBeEQLosTRsJOH9LnEmZW5PzK3cDAkn3BCU1byvVmivpC3ssqS2Car/z/QM=', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 07:22:09 GMT', 'x-amz-request-id': '6B30F1635C22C516', 'server': 'AmazonS3'}}}
{'ResponseMetadata': {'HTTPStatusCode': 204, 'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HostId': 'D4nIam0anNHmLOPG5BBCQUFNCawIM5gttQALtP4IX5iLY0gPl78jy/zo+UcJ6ahOTTKLAJ3he1o=', 'RequestId': 'C97C79B4F0DCAB34', 'HTTPHeaders': {'x-amz-id-2': 'D4nIam0anNHmLOPG5BBCQUFNCawIM5gttQALtP4IX5iLY0gPl78jy/zo+UcJ6ahOTTKLAJ3he1o=', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 07:22:10 GMT', 'x-amz-request-id': 'C97C79B4F0DCAB34', 'server': 'AmazonS3'}}}
{'ResponseMetadata': {'HTTPStatusCode': 204, 'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HostId': 'WIFcb/N7KWR/rJUNrLnn4b3L51At9yge2WQ2XWkw9m98HI54UolBxz3rGme+uoal2mWxXd3Exio=', 'RequestId': 'BCB23562E691A69F', 'HTTPHeaders': {'x-amz-id-2': 'WIFcb/N7KWR/rJUNrLnn4b3L51At9yge2WQ2XWkw9m98HI54UolBxz3rGme+uoal2mWxXd3Exio=', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 07:22:10 GMT', 'x-amz-request-id': 'BCB23562E691A69F', 'server': 'AmazonS3'}}
Delete bucket...
Sample script
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_s3_client = session.client('s3')
s3 = boto3.resource('s3')
for bucket_name in sys.argv[1:]:
bucket = s3.Bucket(bucket_name)
try:
response = bucket.delete()
print response
except Exception as error:
print error
**********************************************************
output:-
(we need to pass bucket name as the parameter)
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./delete_s3.py pythonbucket1-2018-08-29-1535490688
{'ResponseMetadata': {'HTTPStatusCode': 204, 'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HostId': 'oDeaICQ/pP4tNk4Z4SW4LrObKYZIYnQUyPX3UWcU936qskOvPLO1SLesC43orgMZijwjQakpKuY=', 'RequestId': '0ECE4D2E59AE3C43', 'HTTPHeaders': {'x-amz-id-2': 'oDeaICQ/pP4tNk4Z4SW4LrObKYZIYnQUyPX3UWcU936qskOvPLO1SLesC43orgMZijwjQakpKuY=', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 09:28:33 GMT', 'x-amz-request-id': '0ECE4D2E59AE3C43', 'server': 'AmazonS3'}}}
Database creation script
Sample script
*****************************************************************
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_s3_client = session.client('rds')
rds = boto3.client('rds')
try:
response = rds.create_db_instance(
DBInstanceIdentifier='dbserver',
MasterUsername='dbadmin',
MasterUserPassword='******',
DBInstanceClass='db.t2.micro',
Engine='mariadb',
AllocatedStorage=5)
print response
except Exception as error:
print error
******************************************************************
output:-
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./create_db.py
{u'DBInstance': {u'PubliclyAccessible': True, u'MasterUsername': 'dbadmin', u'MonitoringInterval': 0, u'LicenseModel': 'general-public-license', u'VpcSecurityGroups': [{u'Status': 'active', u'VpcSecurityGroupId': 'sg-3fb4834e'}], u'CopyTagsToSnapshot': False, u'OptionGroupMemberships': [{u'Status': 'in-sync', u'OptionGroupName': 'default:mariadb-10-1'}], u'PendingModifiedValues': {u'MasterUserPassword': '****'}, u'Engine': 'mariadb', u'MultiAZ': False, u'DBSecurityGroups': [], u'DBParameterGroups': [{u'DBParameterGroupName': 'default.mariadb10.1', u'ParameterApplyStatus': 'in-sync'}], u'PerformanceInsightsEnabled': False, u'AutoMinorVersionUpgrade': True, u'PreferredBackupWindow': '13:23-13:53', u'DBSubnetGroup': {u'Subnets': [{u'SubnetStatus': 'Active', u'SubnetIdentifier': 'subnet-8fb4f5d5', u'SubnetAvailabilityZone': {u'Name': 'us-west-2c'}}, {u'SubnetStatus': 'Active', u'SubnetIdentifier': 'subnet-d9711ba0', u'SubnetAvailabilityZone': {u'Name': 'us-west-2b'}}, {u'SubnetStatus': 'Active', u'SubnetIdentifier': 'subnet-69188c22', u'SubnetAvailabilityZone': {u'Name': 'us-west-2a'}}], u'DBSubnetGroupName': 'default', u'VpcId': 'vpc-429b8b3b', u'DBSubnetGroupDescription': 'default', u'SubnetGroupStatus': 'Complete'}, u'ReadReplicaDBInstanceIdentifiers': [], u'AllocatedStorage': 5, u'DBInstanceArn': 'arn:aws:rds:us-west-2:891070219291:db:dbserver', u'BackupRetentionPeriod': 1, u'PreferredMaintenanceWindow': 'sat:07:02-sat:07:32', u'DBInstanceStatus': 'creating', u'IAMDatabaseAuthenticationEnabled': False, u'EngineVersion': '10.1.34', u'DomainMemberships': [], u'StorageType': 'standard', u'DbiResourceId': 'db-SF625J6QYBSD6HHUXYUET65YEE', u'CACertificateIdentifier': 'rds-ca-2015', u'StorageEncrypted': False, u'DBInstanceClass': 'db.t2.micro', u'DbInstancePort': 0, u'DBInstanceIdentifier': 'dbserver'}, 'ResponseMetadata': {'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'RequestId': '949eccc0-d3cb-4f62-a0b9-2b465b9c1055', 'HTTPHeaders': {'x-amzn-requestid': '949eccc0-d3cb-4f62-a0b9-2b465b9c1055', 'content-type': 'text/xml', 'content-length': '3647', 'vary': 'Accept-Encoding', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 21:08:10 GMT'}}}
Delete DB instance
Sample script
*****************************************************************
unixchips@unixchips:~$ cat delete_db.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
import boto3
import os
import argparse
import sys
session = boto3.Session(profile_name='default')
default_s3_client = session.client('rds')
rds = boto3.client('rds')
try:
response = rds.delete_db_instance(
DBInstanceIdentifier='dbserver',
SkipFinalSnapshot=True)
print response
except Exception as error:
print error
*********************************************************
output:-
unixchips@unixchips:~$ ./delete_db.py
{u'DBInstance': {u'PubliclyAccessible': True, u'MasterUsername': 'dbadmin', u'MonitoringInterval': 0, u'LicenseModel': 'general-public-license', u'VpcSecurityGroups': [{u'Status': 'active', u'VpcSecurityGroupId': 'sg-3fb4834e'}], u'InstanceCreateTime': datetime.datetime(2018, 8, 29, 21, 8, 10, 389000, tzinfo=tzutc()), u'CopyTagsToSnapshot': False, u'OptionGroupMemberships': [{u'Status': 'in-sync', u'OptionGroupName': 'default:mariadb-10-1'}], u'PendingModifiedValues': {u'MasterUserPassword': '****'}, u'Engine': 'mariadb', u'MultiAZ': False, u'DBSecurityGroups': [], u'DBParameterGroups': [{u'DBParameterGroupName': 'default.mariadb10.1', u'ParameterApplyStatus': 'in-sync'}], u'PerformanceInsightsEnabled': False, u'AutoMinorVersionUpgrade': True, u'PreferredBackupWindow': '13:23-13:53', u'DBSubnetGroup': {u'Subnets': [{u'SubnetStatus': 'Active', u'SubnetIdentifier': 'subnet-8fb4f5d5', u'SubnetAvailabilityZone': {u'Name': 'us-west-2c'}}, {u'SubnetStatus': 'Active', u'SubnetIdentifier': 'subnet-d9711ba0', u'SubnetAvailabilityZone': {u'Name': 'us-west-2b'}}, {u'SubnetStatus': 'Active', u'SubnetIdentifier': 'subnet-69188c22', u'SubnetAvailabilityZone': {u'Name': 'us-west-2a'}}], u'DBSubnetGroupName': 'default', u'VpcId': 'vpc-429b8b3b', u'DBSubnetGroupDescription': 'default', u'SubnetGroupStatus': 'Complete'}, u'ReadReplicaDBInstanceIdentifiers': [], u'AllocatedStorage': 5, u'DBInstanceArn': 'arn:aws:rds:us-west-2:891070219291:db:dbserver', u'BackupRetentionPeriod': 1, u'PreferredMaintenanceWindow': 'sat:07:02-sat:07:32', u'Endpoint': {u'HostedZoneId': 'Z1PVIF0B656C1W', u'Port': 3306, u'Address': 'dbserver.c5g5m1fcix6x.us-west-2.rds.amazonaws.com'}, u'DBInstanceStatus': 'deleting', u'IAMDatabaseAuthenticationEnabled': False, u'EngineVersion': '10.1.34', u'AvailabilityZone': 'us-west-2b', u'DomainMemberships': [], u'StorageType': 'standard', u'DbiResourceId': 'db-SF625J6QYBSD6HHUXYUET65YEE', u'CACertificateIdentifier': 'rds-ca-2010', u'StorageEncrypted': False, u'DBInstanceClass': 'db.t2.micro', u'DbInstancePort': 0, u'DBInstanceIdentifier': 'dbserver'}, 'ResponseMetadata': {'RetryAttempts': 0, 'HTTPStatusCode': 200, 'RequestId': '3dfd0ff6-5f1b-4b79-aea7-4eb868a5bbe1', 'HTTPHeaders': {'x-amzn-requestid': '3dfd0ff6-5f1b-4b79-aea7-4eb868a5bbe1', 'content-type': 'text/xml', 'content-length': '3963', 'vary': 'Accept-Encoding', 'date': 'Wed, 29 Aug 2018 21:12:35 GMT'}}}
We have many more options to automate the AWS management using boto and i will explain in detail in another post.
Thank you for reading ....